(ThyBlackMan.com) African American men have the highest risk of developing oral cancer compared to any other group in the U.S. population. It is a cancer which occurs twice as often in the black population as in whites, and survival statistics for blacks over five years are also poorer at 33%, versus 55% for whites. Most cases of oral cancer are linked to cigarette smoking, heavy alcohol use, or the use of both tobacco and alcohol together. In fact, using tobacco plus alcohol poses a much greater risk than using either substance alone.
Certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) may also play a part in oral cancer. It’s not just smokeless tobacco (“dip” and “chew”). Using tobacco of 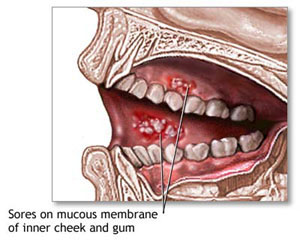 any kind, including cigarettes, puts you at risk for oral cancer, and the risk of only increases with age—most oral cancers occur after age 40. The death rate associated with this cancer is particularly high not because it is hard to discover or diagnose, but due to the cancer being routinely discovered late in its development
any kind, including cigarettes, puts you at risk for oral cancer, and the risk of only increases with age—most oral cancers occur after age 40. The death rate associated with this cancer is particularly high not because it is hard to discover or diagnose, but due to the cancer being routinely discovered late in its development
What Are the Possible Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
• A sore, irritation, lump or thick patch in your mouth, lip, or throat
• A white or red patch in your mouth
• A feeling that something is caught in your throat
• Difficulty chewing or swallowing
• Difficulty moving your jaw or tongue
• Numbness in your tongue or other areas of your mouth
• Swelling of your jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly or become uncomfortable
• Pain in one ear without hearing loss
Be on the lookout for any changes in your mouth, especially if you smoke or drink.
What Should You do if You Have Symptoms?
See a doctor or dentist if any symptoms last more than 2 weeks. Most often, symptoms do not mean cancer. An infection or another problem can cause the same symptoms. But it’s important to get them checked out—because if you do have cancer, it can be treated more successfully if it’s caught early. Ask for an oral cancer exam. It’s quick, painless, and it could save your life.
About Oral Cancer
Cancer is defined as the uncontrollable growth of cells that invade and cause damage to surrounding tissue. Oral cancer appears as a growth or sore that does not go away. Oral cancer — which includes cancers of the lips, tongue, cheek, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and pharynx (throat) — can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early.
The Oral Cancer Exam
An oral cancer examination can detect early signs of cancer. The exam is painless—and takes only a few minutes. During the exam, your doctor or dentist will check your face, neck, lips, entire mouth, and the back of your throat for possible signs of cancer.
Written by Karissa Lang

















The Oral Cancer Foundation is working with over a thousand dental practices in the US during April (oral cancer awareness month) to provide free oral cancer screenings to the public in their communities. Please check our calendar at this link to find a location near you.
http://www.oralcancer-screening.org/events/
For more details about the early signs and symptoms, detailed discussions of risk factors for developing it, and more information, please visit the non-profit OCF website to learn more. http://www.oralcancer.org